Research
Our lab takes a comprehensive view of the current state of energy systems and environmental problems from a variety of aspects, presents system methods to deal with them, and conducts research to ensure the sustainable development of human beings.
We are especially specialized at interdisciplinary research: Specifically, while taking into consideration global warming countermeasures and environmental contribution activities and social implementation of the system, our research includes a wide range of techniques to contribute to the environment, including engineering, economics and behavioral science.
I want you to start with a clear sense of problem in your research and consider what you need to do to solve problems.

Research Projects
Our laboratory focuses on interdisciplinary studies that bridge environmental sustainability, energy systems optimization, and social dynamics. Key areas of our research include:
Quantitative Environmental Assessments: Investigating indicators such as carbon footprints and their interactions within societal frameworks.
Municipal-Level Energy Optimization: Designing energy supply systems that effectively balance decarbonization goals with economic efficiency.
Agrivoltaics (Solar Sharing): Conducting practical demonstrations and analyzing systems that sustainably integrate agricultural productivity with solar power generation.
Consumer Environmental Preferences: Applying market research techniques to quantify consumer preferences, evaluating the potential for broader adoption of eco-friendly products and practices.
Decarbonization Technology Integration: Developing optimal matches between renewable energy technologies (such as biofuels and solar power) and diverse energy demands, including electricity and liquid fuels.
Current Research Projects
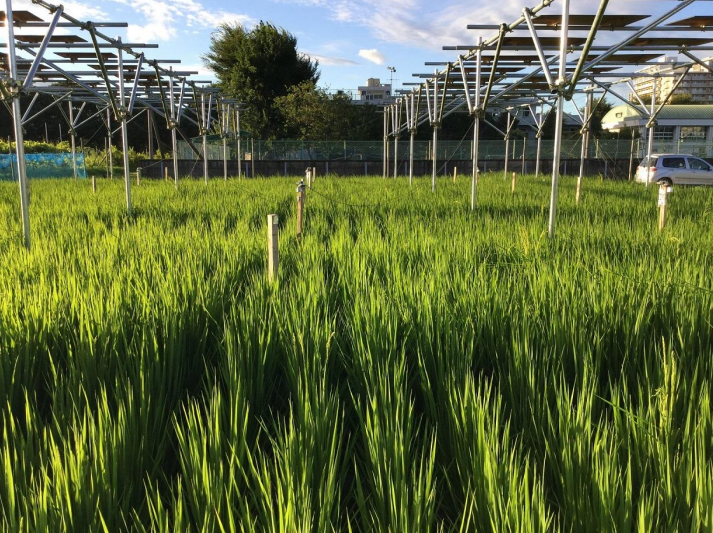

Sustainable Integration of Food and Energy Systems
With suitable land for solar power decreasing, agrivoltaics —a system combining agricultural production and solar power generation—is gaining global attention. The potential for agrivoltaics in Japan is significant; covering only 4% of Japan’s farmland could theoretically double the nation’s solar power capacity. For farmers, this approach offers a valuable, stable secondary income independent of agricultural market fluctuations.
Yet, agrivoltaics’ full potential depends heavily on its integration with existing electrical grids. Our research addresses critical issues like power variability, surplus electricity management, and necessary curtailment through advanced grid simulations. Insights from these studies guide effective policy and infrastructure planning.
Current Research Highlight:
We examine vertical solar panels, which generate electricity during morning and evening hours, unlike traditional horizontal installations. Field trials at the University of Tokyo’s Tanashi farm are currently underway to evaluate the impact of these vertical installations on agricultural yields, alongside grid integration assessments.
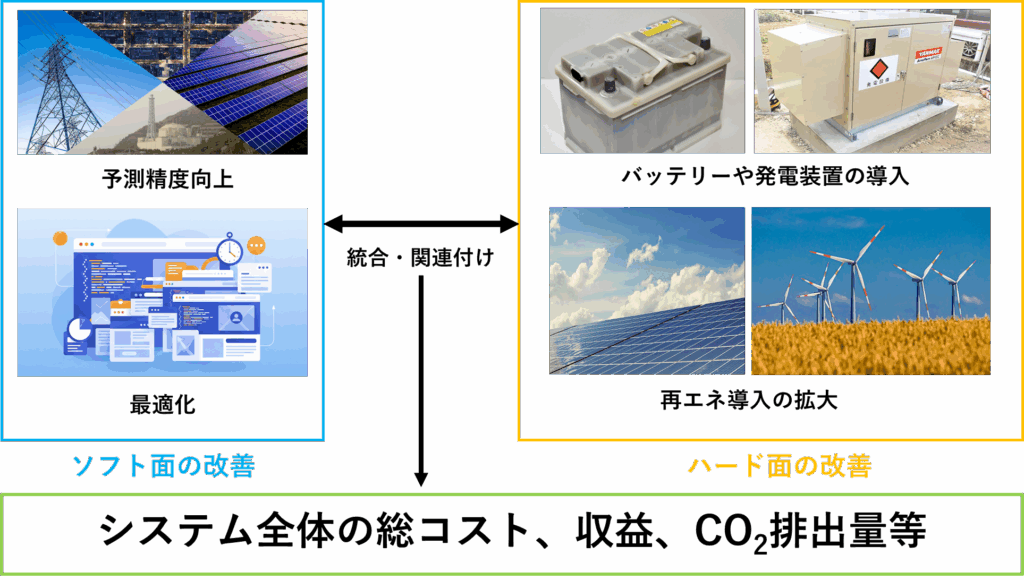
Integrated Optimization of Energy Systems
Renewable energy sources, especially solar power, play a critical role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. However, their inherent variability—due to weather dependency—poses significant challenges compared to conventional energy sources. To address these challenges, our research employs two complementary approaches:
Software Solutions: Enhancing grid operation efficiency through improved forecasting of renewable energy outputs, electricity demand, and dynamic market pricing, complemented by advanced optimization algorithms.
Hardware Solutions: Optimizing the physical infrastructure by integrating energy storage solutions (batteries) and decentralized generation systems.
Recognizing the need for integrated solutions, our lab merges both software and hardware analyses using real-world utility data, aiming to comprehensively evaluate impacts on total system costs and greenhouse gas emissions.
Current Research Highlight:
We quantitatively assess the effects of improved prediction models for solar generation, electricity demand, and market pricing (JEPX) on overall energy system costs and optimal battery capacity.
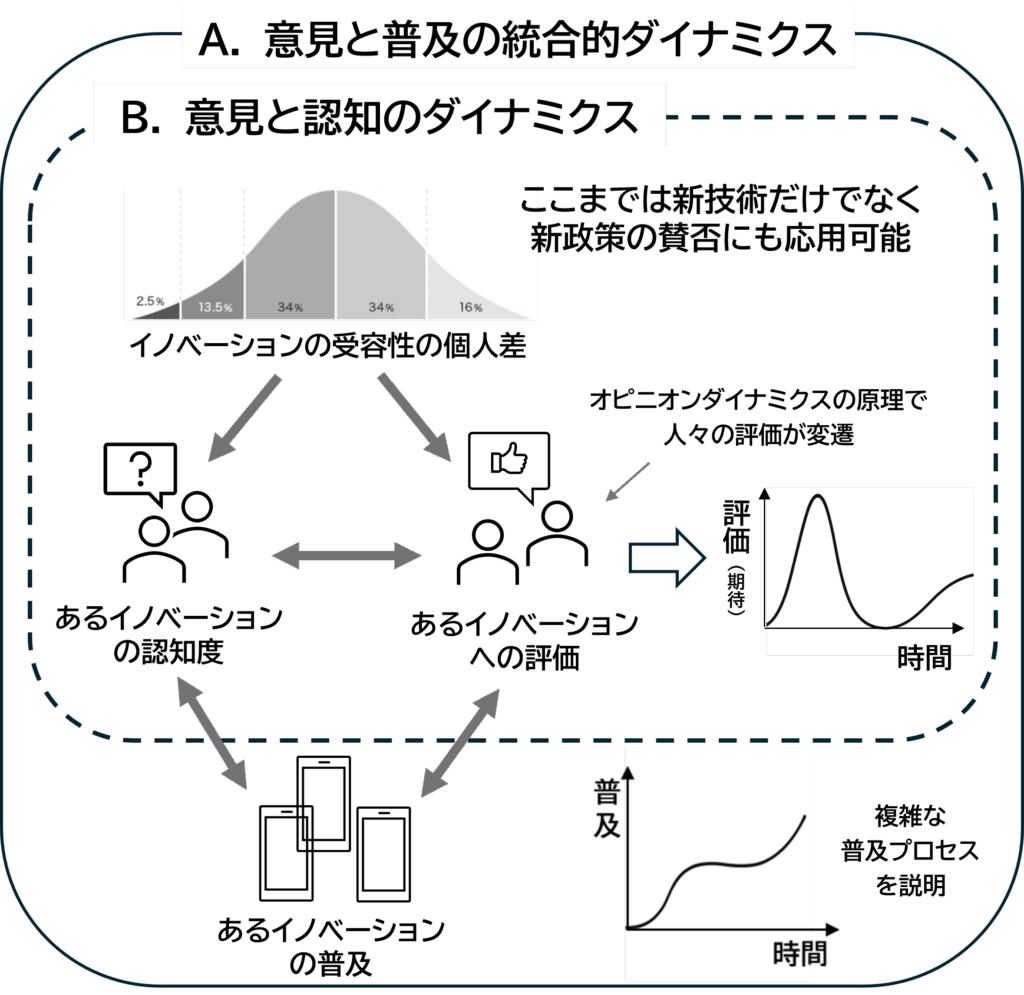
Dynamics of Environmental Technology Adoption
The effectiveness of any environmental technology hinges significantly on societal acceptance and adoption. However, consumer decisions often deviate from purely rational evaluations based on environmental benefits or economic savings. Instead, they may be influenced by social and psychological factors such as perceptions, social norms, trust, and reputational influences.
Our laboratory leverages the theoretical frameworks of opinion dynamics and bounded rationality to analyze how consumer preferences and evaluations evolve over time, impacting technology adoption rates. By understanding these dynamics, we aim to identify and propose effective policy measures to accelerate the widespread adoption of essential environmental technologies.
Current Research Highlight:
Our team employs agent-based modeling (ABM), mathematical simulations, and empirical analyses to track and explain shifts in consumer preferences toward various environmental innovations (e.g., EVs)